Accoppiamento DC vs AC: capire le differenze
Indice dei contenuti
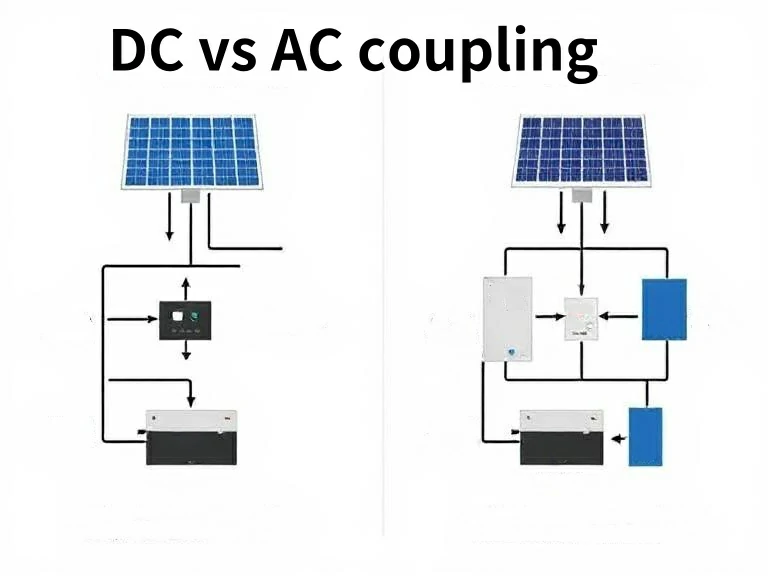
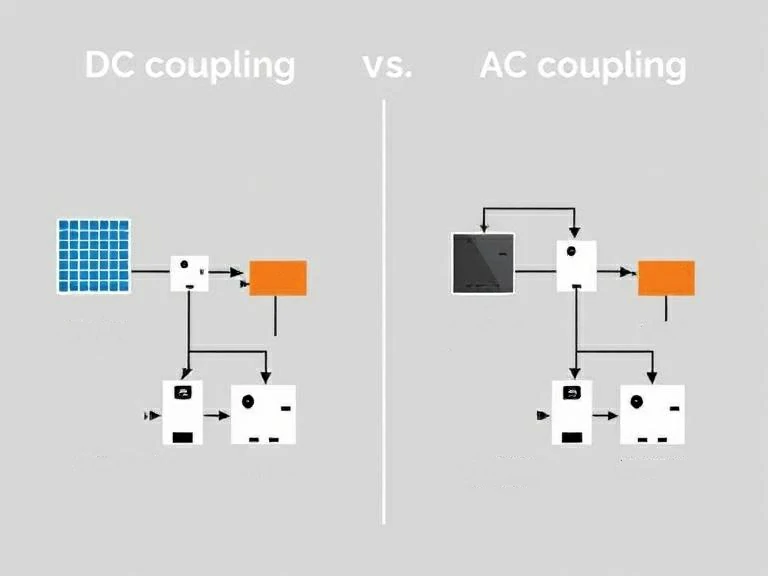
Conoscere la distinzione tra Accoppiamento DC vs AC è fondamentale sia nei sistemi di alimentazione che nei circuiti elettronici. L'accoppiamento in corrente continua prevede il collegamento dei pannelli solari al sistema di batterie ed è ideale per le applicazioni off grid, mentre l'accoppiamento in corrente alternata utilizza un inverter per collegare i pannelli solari alla batteria, offrendo flessibilità e convenienza per l'integrazione in sistemi preesistenti, come le configurazioni grid tied.
Questo articolo approfondirà il confronto tra Accoppiamento DC vs AC per aiutarvi a determinare l'opzione più adatta alle vostre esigenze, esaminando aspetti quali l'efficienza dell'installazione e la scalabilità, nonché le soluzioni di alimentazione di backup per determinare il metodo più adatto alle vostre esigenze.

Che cos'è l'accoppiamento nei sistemi di energia solare?
Una gestione efficiente dell'energia è fondamentale per i sistemi energetici, grazie all'uso di tecniche di accoppiamento dei segnali, che giocano un ruolo fondamentale nell'ottimizzazione delle nostre configurazioni solari, in particolare se si considerano le differenze tra i sistemi solari e i sistemi di monitoraggio. Accoppiamento DC vs AC.
Definizione e scopo
Nei circuiti, sia in corrente continua (DC) che in corrente alternata (AC), l'accoppiamento comporta il trasferimento di energia per garantire il funzionamento regolare del sistema; la scelta ottimale, tra Accoppiamento DC vs AC può avere un impatto molto importante sulle prestazioni di un sistema elettrico.
Ruolo dell'accoppiamento nei sistemi off-grid e grid-tied
I sistemi off grid si basano molto sul concetto di accoppiamento per raggiungere con successo l'indipendenza energetica; l'accoppiamento in corrente continua è una scelta dovuta alla sua compatibilità con le batterie in queste configurazioni. Al contrario, i sistemi grid tied optano per l'accoppiamento in corrente alternata per stabilire una connessione con la rete. La distinzione tra Accoppiamento DC vs AC diventa evidente nel contesto di questi sistemi, sottolineando l'importanza della selezione del tipo.
L'importanza e l'impatto della scelta tra accoppiamento CC e CA
Scegliere tra Accoppiamento DC vs AC influisce su molti aspetti, come l'efficienza e il costo. L'accoppiamento in c.a. è ottimo per aggiungere facilmente sistemi esistenti. Ma l'accoppiamento in corrente continua è migliore per le nuove installazioni perché è più efficiente. È fondamentale capire la differenza tra accoppiamento CC e CA e i loro vantaggi. Aiuta a creare un sistema solare che soddisfi i vostri obiettivi di sostenibilità.
Che cos'è l'accoppiamento in corrente continua?
L'accoppiamento in c.c. prevede che sia la componente di corrente alternata (c.a.) che quella di corrente (c.c.) di un segnale passino attraverso un elemento di accoppiamento senza alcuna interruzione dell'impedenza o processo di filtraggio.
Come funziona l'accoppiamento CC
L'accoppiamento in corrente continua funziona collegando la sorgente del segnale al terminale di ingresso del dispositivo ricevente, come un oscilloscopio o un amplificatore, senza alcun condensatore che possa ostacolare la parte in corrente continua del flusso del segnale; questo metodo di connessione diretta si contrappone a Accoppiamento DC vs ACmentre l'accoppiamento in c.a. coinvolge tipicamente condensatori che bloccano la componente c.c. del segnale, lasciando passare le componenti c.a..
Componenti di un sistema accoppiato in c.c.
In genere, in un sistema collegato in c.c. si trovano questi componenti;
La sorgente del segnale è responsabile della creazione del segnale da inviare; può essere costituita da elementi in corrente alternata (CA) e in corrente continua (CC).
Per quanto riguarda l'elemento di accoppiamento, di solito si tratta di un condensatore o di un induttore che, nel caso dell'accoppiamento in corrente continua, presenta un'impedenza elevata per i segnali in corrente continua ma consente il passaggio dei segnali in corrente alternata. Tuttavia, è importante notare che nelle implementazioni pratiche di accoppiamento in c.c., l'elemento di accoppiamento potrebbe non bloccare attivamente i segnali in c.c., ma consentirne il passaggio grazie al collegamento diretto.
Il dispositivo ricevente può essere un amplificatore o un oscilloscopio o qualsiasi altra apparecchiatura utilizzata per monitorare o analizzare il segnale trasmesso attraverso di esso in un sistema accoppiato in c.c., dove può gestire efficacemente sia gli aspetti in c.a. che in c.c. del segnale.
Vantaggi dell'accoppiamento CC
I vantaggi dell'accoppiamento in corrente continua includono:
Mantiene intatta l'integrità del segnale utilizzando l'accoppiamento CC per preservare il segnale insieme alla sua componente CC, per esigenze di analisi ed elaborazione accurate.
I circuiti di accoppiamento in c.c. sono piuttosto semplici e chiari, poiché necessitano di parti rispetto ai circuiti di accoppiamento in c.a.. L'accoppiamento in c.c. offre versatilità per usi quali il lavoro con segnali a bassa frequenza e segnali in corrente continua.
Svantaggi dell'accoppiamento CC
Sebbene l'accoppiamento in corrente continua offra dei vantaggi, presenta anche degli svantaggi.
Nei circuiti con stadi di amplificazione, come i circuiti amplificati, l'accoppiamento in corrente continua può provocare una deriva dello zero in cui le alterazioni di fattori come la temperatura o l'invecchiamento dei componenti possono influire sulle caratteristiche operative stabili degli stadi del circuito.
Quando si utilizza un accoppiamento CC che permette al segnale di passare senza controllo, qualsiasi offset o rumore CC esistente, proveniente dalla sorgente del segnale, potrebbe disturbare l'elaborazione o l'analisi del segnale.

Non c'è un punto di guasto centrale in un sistema accoppiato in CA (usando un Inverter accoppiato in CA). Se il inverter solare ibrido Se un sistema ad accoppiamento CC si guasta, tutto si ferma. In un sistema accoppiato in corrente alternata, i pannelli solari continueranno a fornire elettricità all'abitazione indipendentemente da ciò che accade alla batteria, grazie alla mancanza di un punto di guasto centrale.

In breve, l'accoppiamento in c.c. comporta la trasmissione di segnali mantenendo sia la componente in c.a. che quella in c.c.; sebbene abbia dei vantaggi, come il mantenimento dell'integrità del segnale e la semplicità, presenta anche degli svantaggi, come la tendenza alla deriva e ai problemi di interferenza. La scelta tra l'accoppiamento CC e l'accoppiamento CA dipende dalle esigenze della situazione reale.
Che cos'è l'accoppiamento CA?
In termini elettronici, l'accoppiamento CA comporta la configurazione di un circuito che impiega un condensatore per trasmettere i segnali tra le sezioni del circuito; questa configurazione permette di far passare solo la parte CA (corrente alternata) del segnale, mentre ostacola la parte CC (corrente continua), il che mette in evidenza una delle differenze chiave tra Accoppiamento DC vs AC.
Come funziona l'accoppiamento CA
Quando un condensatore viene inserito nel percorso in serie con altri componenti, funziona come un filtro per i segnali CA ad alta frequenza che possono passare, mentre ostacola i segnali CC a bassa frequenza e qualsiasi segnale CA al di sotto del punto di taglio della frequenza designato dal condensatore.
Componenti di un sistema accoppiato in CA
Una normale configurazione con accoppiamento in c.a. comprende di solito queste parti;
- Circuito sorgente: Il circuito che genera il segnale da accoppiare.
- Condensatore di accoppiamento: Il condensatore che blocca la componente CC e lascia passare la componente CA del segnale.
- Circuito di carico: Il circuito che riceve ed elabora il segnale CA.
Vantaggi dell'accoppiamento CA
I vantaggi dell'accoppiamento CA comprendono:
- Eliminazione delle compensazioni DC: L'accoppiamento CA elimina qualsiasi distorsione di corrente (CC) nel segnale per facilitare l'analisi e la misurazione della componente di corrente alternata (CA).
- Isolamento dei componenti CC: Separa i componenti del segnale per evitare che influenzino il funzionamento del circuito di carico.
- Maggiore chiarezza del segnale: When you eliminate DC offsets from the signal through AC coupling process; it enhances the clarity of the AC signal which facilitates observation and analysis.
- Flexibility in Amplifier Design: AC coupling provides freedom in crafting amplifiers since the DC operating point of each stage can be fine tuned independently.
Svantaggi dell'accoppiamento CA
The disadvantages of AC coupling include:
- Loss of DC Information: AC coupling eliminates the current (DC) part of the signal, for specific applications where this is crucial.
- Potential for Low-Frequency Signal Loss: Depending on the capacitance of the coupling capacitor used in the circuitry the frequency AC parts of the signal could potentially be reduced or even disappear altogether.
- Complexity in Signal Reconstruction: If the DC part is crucially important in this case it could be quite challenging or even impossible to recreate the initial signal, from its AC coupled counterpart.
To sum it up quickly, AC coupling proves handy for separating DC elements and studying AC signals in circuits; yet it does have its drawbacks such, as signal loss and the incapacity to retain DC details.
Principali differenze tra accoppiamento CA e accoppiamento CC
Comparing Accoppiamento DC vs AC involves understanding how they operate in scenarios and their effectiveness in terms of installation ease and scalability along, with backup power capabilities.
Efficienza e perdite di conversione
Efficienza:
DC connected systems could be more efficient as they link directly to DC sources and lessen the requirement for converting AC to DC, which may cause energy losses. In contrast, AC connected systems involve AC to DC conversion, which might lead, to losses. This contrast highlights the key differences between Accoppiamento DC vs AC.
Conversion Losses:
DC coupled systems generally have lower conversion losses because they minimize the number of conversion steps. AC coupled systems may experience higher conversion losses due to the additional AC-to-DC conversion process, but advancements in technology are continually reducing these losses.
Complessità e costi di installazione
Installation Complexity:
DC coupled systems might necessitate preparation and specialized knowledge when being installed to guarantee electrical safety and compatibility compared to AC coupled systems that are usually simpler to install and can be scaled up easily by incorporating more battery modules akin, to setting up common household appliances.
Costo:
The price can differ depending on the system and setup you choose to go with; DC coupled systems might require more upfront investment because of the specialized installation and setup they need.
In contrast, AC coupled systems could be a more budget-friendly option in certain situations, thanks to their easier installation process and scalability potential. This difference in pricing and installation complexity highlights one of the key aspects of Accoppiamento DC vs AC.
Scalabilità e retrofitting
Scalabilità:
DC connected systems may require pre planning for scalability purposes while AC connected systems offer greater flexibility, for scaling by enabling the incorporation of extra battery modules as required.
Retrofitting:
AC linked systems are usually simpler to integrate into solar setups since they don’t need major alterations to the existing DC system in place already! This ease of integration is one of the advantages of Accoppiamento DC vs AC; however, for DC connected systems, it might be trickier to retrofit due to the need for redesigning or adjustments to the current DC system.
Capacità di alimentazione di backup
Backup Power:
DC coupled systems can provide power solutions by connecting, to DC sources and potentially offering instant power in case of grid failures.
AC coupled systems utilize inverters to change current into alternating current for home or business applications; this process could cause a slight delay, in instances of grid breakdowns though contemporary inverters usually respond swiftly and are equipped with backup features.
Both AC coupled and DC coupled systems come with their set of pros and cons that should be considered based on the application context they will be used in, along with factors like installation requirements, cost considerations, as well as the need for efficiency and scalability; understanding these trade-offs is crucial when evaluating Accoppiamento DC vs AC for a particular application.

Accoppiata CA e accoppiata CC: Qual è la soluzione giusta per voi?
Looking at Accoppiamento DC vs AC and making the best choice can pose a challenge at times; knowing the benefits and the right ways to use them can make it easier for homeowners or business owners to handle their finances wisely.
Considerazioni per i proprietari di case
Homeowners frequently decide between AC coupled vs DC coupled systems based on their preferences and needs alongside their current setup and energy demands.
When it comes to the electrical setup in a house or building. AC coupled systems are usually simpler to incorporate since they utilize the existing AC wiring in place already with minimal interruptions when being installed.
To achieve energy self-sufficiency and reduce reliance on the grid for grid or partially off grid residences focusing on energy independence could be more beneficial with DC coupled systems that directly link DC sources such as solar panels and battery storage units can lead to potential cost savings, on electricity bills.
Applicazioni commerciali e industriali
In industrial environments the choice, between AC coupled vs DC coupled systems becomes more intricate because of the intricacy and magnitude of operations.
Large scale energy systems are common in industrial settings and can benefit from using DC coupled systems, for improved efficiency when working with high voltage DC (HVDC) reducing energy loss over extended distances.
In general, for maintenance and reliability concerns with AC coupled vs DC coupled systems differ. DC systems typically need maintenance due, to their simpler circuits while AC systems may provide more reliable backup power and seamless grid integration especially in crucial infrastructure scenarios.
Bilancio e considerazioni a lungo termine
Financial limitations and strategic foresight are factors, in deciding the most effective method of coupling, whether it be Accoppiamento DC vs AC, over an extended period.
AC coupled systems usually come with a higher initial cost since they are easier to connect to existing infrastructure compared to DC coupled systems which may require more upfront investment due to the necessity of new wiring and possibly extra equipment in the long term, for better efficiency.
Long term expenses can be reduced with DC coupled systems because they are more efficient and experience energy loss compared to other options available in the market today; this can result in savings for businesses operating on a larger scale such, as commercial and industrial settings.
DC connected setups provide adaptability for upcoming expansions and the assimilation of novel technologies like electric vehicles (EVs) along with extra renewable energy sources integration in the mix as well. As advancements progress, a rise in DC systems’ prevalence may occur alongside a range of benefits, making Accoppiamento DC vs AC an important consideration for future-proofing energy systems.
Esempi pratici e casi d'uso
In the field of electronics and signal processing, the use of coupling techniques is very important in shaping how signals pass between circuits; here we explore real-world examples and practical applications for each method, as well as systems that blend elements of both Accoppiamento DC vs AC.
Quando utilizzare l'accoppiamento CC
DC coupling involves transmitting both the alternating (AC) and current (DC) parts of a signal. This is different, from AC coupling, which only transmits the AC part of the signal and helps to distinguish between Accoppiamento DC vs AC.
Practical Examples:
AC coupling is, about sending the alternating current part of a signal while filtering out the direct current component; this method proves handy in situations where the direct current level isn’t important or could lead to disruptions.
Data Converters typically utilize DC coupling to preserve the DC level within the signal during the conversion process with Analog to digital converters (ADCs) and digital, to analog converters (DACS).
Operational amplifier circuits often utilize current (DC coupling) like in voltage follower and integrator circuits that maintain the input signals DC component, in the output signal.
Quando utilizzare un accoppiamento CA
AC coupling is, about sending the alternating current part of a signal while filtering out the direct current component; this method proves handy in situations where the direct current level isn’t important or could lead to disruptions.
Practical Examples:
AC coupling is commonly employed in systems like telecommunications and communication networks such as telephone lines to differentiate the DC fluctuations, between network segments.
In mixing consoles and line level audio interfaces AC coupling is commonly employed to eliminate any DC offset that could, potentially create issues in later parts of the signal flow.
In RF (radio frequency circuits and frequency signal processing AC coupling is commonly used to safeguard the AC signal from being influenced by DC components.
Sistemi ibridi: Combinazione di accoppiamenti CA e CC
Hybrid systems combine AC and DC coupling to deliver efficiency and flexibility ideal for setups that need adaptability and backup solutions in scenarios like those where high efficiency and seamless integration, with existing setups are needed; hybrids are a valuable option when considering Accoppiamento DC vs AC.
They use DC coupling for new solar arrays and keep existing AC systems. This setup boosts energy efficiency, provides strong backup power, and increases system resilience.
Conclusione
We’ve delved into the distinctions between AC coupled vs DC coupled systems here; understanding the contrast between Accoppiamento DC vs AC is essential for utilizing power, in residential or professional settings. We’ve discussed the mechanics of DC coupling including its components well as its pros and cons; moreover, we have outlined the workings of AC coupling along with its components benefits and potential challenges.
We’ve gone over the distinctions between Accoppiamento DC vs AC such as effectiveness and the simplicity of installation. This contrast assists in making a more informed decision, for you whether you’re a homeowner or overseeing a business establishment; understanding these specifics holds significance as it enables you to pinpoint the ideal resolution that aligns with your requirements and financial resources.
Deciding to opt for Accoppiamento DC vs AC depends on your requirements and preferences; some individuals may consider a combination of both options advantageous for their needs and goals in this regard. Reflecting on these considerations alongside instances can better equip you to arrive at, a judicious decision.
Businesses such as AFORE offer tailored solutions catering to solar energy demands. Leveraging this insight for making environmentally conscious decisions paves the way, towards a sustainable future.
FAQ
Che cos'è l'accoppiamento nei sistemi a energia solare?
In power systems the term coupling refers to transferring energy from solar panels to storage or the grid; this transfer can occur in either current (DC) or alternating current (AC).
Come funziona l'accoppiamento in corrente continua?
DC coupling involves linking panels to batteries and inverters through direct current (DC) a configuration that enhances efficiency especially in, off grid setups.
Quali sono i vantaggi dell'accoppiamento in corrente alternata?
AC coupling makes it easy to connect with the grid, expand systems, and update older ones. It’s great for systems needing to match the grid’s standards.
What are the key differences between DC vs AC coupling?
The key differences between Accoppiamento DC vs AC are that AC coupling is more flexible and easier, to integrate with the grid; DC coupling is more efficient with fewer losses. AC coupling is better for grid-tied systems, while DC is ideal for off-grid.
What are the long-term considerations when deciding between DC vs AC coupling?
When choosing between DC and AC coupling options for your setups needs and future plans, keep, in mind that AC might offer adaptability, for modifications while DC could help reduce expenses and enhance overall performance.