A Guide to Choosing the Best Inverter for Solar Panels
Table of Contents
Selecting the inverter for solar panels is vital as it plays a significant role, in optimizing the efficiency of your solar panel setup – whether it’s for residential use or, off grid applications; having a good grasp of inverters is essential.
Inverters convert the direct current (DC) from the panels into alternating current (AC) making sure that our homes are powered by a source of renewable energy.
For any panel system rated over 5 watts in capacity, an inverter is necessary. There exist kinds, such as, off-grid inverters and pure sine wave inverters. Choosing the one can significantly enhance the systems performance.
These gadgets drive appliances ranging from refrigerators to devices, ensuring efficient energy utilization and safeguarding our investments, in solar technology.
Let’s dive into the kinds of inverters and what they do when it comes to panels purchasing considerations. It’s all about making a smart decision for your solar power setup to run smoothly and cater to your energy requirements effectively. If you would like to know more about inverter for solar panels, please visit AFORE for detailed information.
What Is an Inverter for Solar Panels?
Understanding the core of an energy setup involves getting a grasp, on what an inverter for solar panels does. How it functions – essentially converting direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can power our households and workplaces effectively.
Selecting notch and effective inverter for solar panels plays a role, in maximizing the performance of our solar panel setups. Solar inverters consist of a power conversion component and a monitoring interface that aid, in monitoring the efficiency of the inverter.
Solar power inverters work similar to bridges by linking energy to the electricity that powers our daily lives.
The Definition and Function of a Solar Inverter
A solar inverter serves to manage power and ensure the efficiency of power in rooftop solar systems by producing energy at varying frequencies—unlike traditional steam based generators.
There are kinds of inverters available such as string inverters and microinverters which offer different levels of efficiency and costs while varying in terms of usability as well.
The definition and function of an inverter for solar panels show how crucial they are for solar energy systems. They make these systems work well and efficiently; it is very important to pick a high-quality inverter that fits the needs of each installation.
Why You Need a High-Quality and Efficient Solar Inverter
Having a notch and effective inverter for solar panels is crucial, for various reasons;
- Energy Efficiency: Using an inverter for solar panels that reduces energy wastage when converting power, from solar panels into electricity and allows for more effective utilization of the generated power.
- Reliability and Longevity: A well-made inverter is designed to withstand the elements and operate reliably for many years; this reduces the risk of downtime and the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
- Advanced Features: Top notch inverters frequently include functionalities, like Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) which fine tunes the power output, from panels to suit varying environmental factors.
- System Integration and Compatibility: An inverter that works well with parts of the energy system, like solar panels and batteries is important, for smooth integration and operation.
Key Components of a Solar Inverter
Solar inverters can consist of parts based on their type and structure. However, some key components that are typically present, in inverters are as follows;
- Power Conversion Circuitry: This is the heart of the inverter for solar panels, responsible for converting DC to AC; it may include transformers, capacitors, inductors, and semiconductor devices such as transistors or diodes.
- Control System: The control system oversees the functioning of the inverter to make sure it efficiently and securely converts power, by using microcontrollers and sensors along, with parts.
- Cooling System: Inverter for solar panels produces heat while running; therefore, it is essential to have a cooling system in place like fans or heat sinks to avoid overheating and maintain performance quality.
- Protection Devices: Devices, like fuses and circuit breakers are essential for protecting the inverter and the connected solar energy system from any damage caused by faults or unusual conditions.
- Communication Interface: Today’s inverter for solar panels frequently comes equipped with communication interfaces that allow them to connect with monitoring systems like smartphones or computers, for tracking and management tasks.
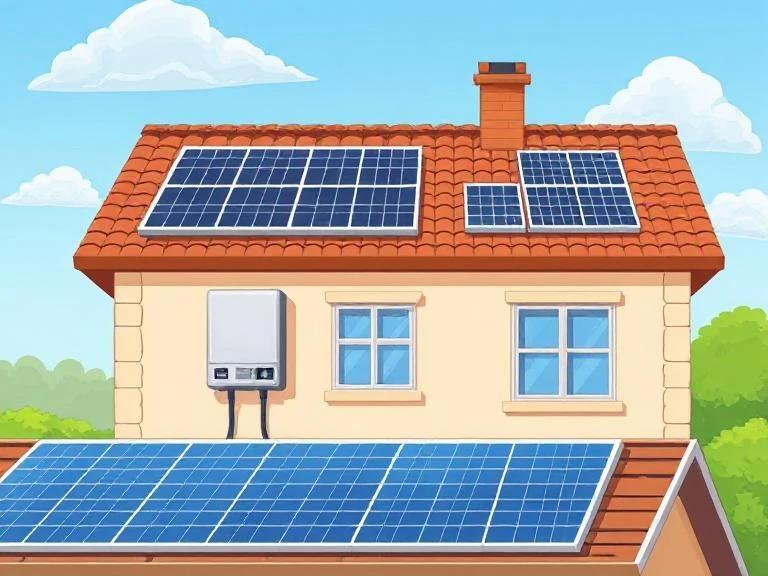

Types of Inverters for Solar Panels
Solar panels generate Direct Current (DC) electricity, which needs to be converted into Alternating Current (AC) for most household and industrial uses; this conversion is facilitated by inverter for solar panels, which comes in various types suited to different applications and system configurations. Below is an overview of the main types of inverters used in solar energy systems.
String Inverters
String inverters are designed to connect multiple solar panels (typically strung together in series) to a single inverter.
Key Features:
- Efficiency: High performance string inverters can reach efficiencies exceeding 96%.
- Cost-Effectiveness: When it comes to cost effectiveness, for power systems string inverters are often seen as a wallet friendly choice.
- Simplicity: They are relatively simple, to install and maintain.
- Applications: Suitable, for both commercial settings with solar panels, in place.
Drawbacks:
- Single Point of Failure: If the inverter stops working it could impact all the panels in the string.
- Shadowing and Panel Mismatch: Differences in shading across panels or variations in their performance levels may lead to a decrease in the efficiency of the system.
Microinverters
Microinverters are small inverters that are installed with each individual solar panel.
Key Features:
- Independence: Each solar panel functions autonomously to reduce the effects of shading or mismatched panels, on the performance of the system.
- Efficiency: Microinverters enhance the power generation of panels to improve the effectiveness of the system.
- Safety: Lower DC voltages reduce the risk of fire or electrical hazards.
- Monitoring: Provides detailed monitoring of each panel’s performance.
Drawbacks:
- Cost: On average microinverters are pricier, per panel compared to string inverters.
- Complexity: Installation and upkeep might become trickier because of the inverters required potentially adding to the complexity of the process.
Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid inverters merge the capabilities of an inverter and a battery charger/inverter, into one device.
Key Features:
- Dual Functionality: It can convert DC electricity from power into AC to be used right away or store it in batteries, for future use.
- Energy Independence: Energy self-sufficiency ensures a power source, in case of grid failures.
- Efficiency: Efficiency is enhanced in inverters through the utilization of sophisticated MPPT algorithms to maximize energy collection.
Drawbacks:
- Cost: Hybrid inverters usually come with a price tag compared to inverters.
- Complexity: Utilizing functions together could raise the level of complexity. Require specific maintenance expertise.
Power Optimizers vs. Inverters
Power Optimizers:
- Function: Power optimizers are devices installed between solar panels and the inverter. They optimize the power output of each panel individually, addressing issues such as shading and panel mismatch.
- Advantages: Improve system efficiency and provide detailed monitoring of panel performance.
- Limitations: Do not convert DC to AC; an inverter is still required.
Inverters:
- Function: Transforming the power produced by panels into alternating current electricity.
- Advantages: An element, in powering systems that provide AC electricity for use.
- Combination Use: Merge power optimizers, with inverters, in your system setup you can boost its efficiency.
To sum up, the decision of which type of inverter for solar panels to use in an energy setup relies on factors, like system size and cost constraints along with energy independence and monitoring needs taken into account; string inverters are a fit for systems due to their cost effectiveness while microinverters offer more independence and better efficiency for individual panels. Here AFORE Single Phase PV String Inverter is highly recommended for residential use.

Hybrid inverters come into play, for applications requiring power and dual functionality that cater to energy setups. Power optimizers can be added alongside inverters to boost system performance and monitoring capabilities further. AFORE Hybrid Solar Inverters are absolutely a good choice for you if you would like to have a hybrid inverter for solar panels.

How to Choose the Best Inverter for Solar Panels?
Selecting the inverter for solar panels is essential to maximize energy output and guarantee system dependability while meeting your unique energy requirements. Here are some important factors and instructions to assist you in choosing the right option.
Key Features to Consider
- Efficiency: prioritize the inverter for solar panels with high efficiency ratings for energy conservation during the conversion from DC, to AC power.
- Compatibility: Make sure the inverter works well with the type and quantity of panels you own and any batteries or grid connection devices you intend to utilize.
- Durability and Warranty: opt for one, from a known manufacturer that offers a warranty and is tailored to endure the specific weather conditions, in your area.
- Monitoring and Control Capabilities: Check out the monitoring and control options, in inverters as they often include advanced features for system monitoring, in real time and remote control based on your requirements.
- Certifications and Compliance: Check the inverter for solar panels to make sure it complies with all the safety and performance standards and certifications, in your region.
- Scalability: If you are considering expanding your power system in the future choose an inverter that’s compatible, with both panels and batteries.
Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid Inverters
Grid-Tied Inverters:
- Function: Convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into the AC electricity that aligns with the power grid requirements.
- Advantages: Being budget friendly and enabling surplus energy to be resold to the grid while ensuring electricity supply throughout the day.
- Limitations: The need for access to the power grid and potential lack of power availability during emergencies unless backup equipment is, on hand.
Off-Grid Inverters:
- Function: Transform DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) and they often come equipped with the ability to charge batteries, for standalone power systems.
- Advantages: Achieve energy independence and ensure power supply when the grid is down.
- Limitations: Higher costs attributed to the necessity of batteries and independent system parts and potential additional maintenance needs.
Sizing Your Solar Inverter Correctly
- Calculate Your Energy Needs: Determine the total wattage of AC power you need to supply your home or business. Consider peak usage times and any future energy needs.
- Assess Your Solar Panel Output: Determining the DC power production of your panels in standard test conditions (STCs). Take into account reductions, in output due to factors like shade coverage on panels and their positioning in relation to the suns path and temperature variations.
- Choose an Appropriately Sized Inverter: Select the right size for your solar panels; make sure it can handle peak power and matches or slightly exceeds the total DC power output of your panels for, off grid setups. Don’t forget about the battery storage capacity and how much energy you’ll need.
- Allow for Future Expansion: Ensure that you select an inverter for solar panels, with a power rating if you intend to expand your panel setup in the future to support any potential growth.

Installation and Maintenance of a Solar Inverter
Solar inverters play a role in energy systems by converting the DC power produced by solar panels into AC electricity for both residential and industrial purposes. Properly installing and maintaining inverters is key to their dependable performance.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
- Preparation: Make sure you have all the product accessories and tools, for installation, at hand before starting. Make sure that the installation setting aligns with the criteria set by the manufacturer.
- Mechanical Installation: Make a plan, for how to set up the installation and make sure the inverter is transported and placed correctly. Ensure the inverter is securely fastened in position using mounting brackets or other suitable supports.
- Electrical Wiring: Make sure to connect the DC side cables to the panels, with the polarity and link the AC side cables to either the grid or the load as needed. Don’t forget to ground them and connect any communication cables if necessary.
- Inspection and Testing: Please make sure to check all the connections and wiring to confirm they are secure and accurate then proceed with tests to validate the proper functioning of the inverter as intended.
- Commissioning and Operation: After finishing the setup and conducting tests successfully it’s time to launch the system and start using it. Keep an eye out for how the system performs and make any tweaks as needed.
Best Practices for Solar Inverter Maintenance
- Regular Inspections: Make sure to inspect the inverter and its connections frequently to ensure they are, in shape and working well. Look out for any signs of wear and tear or damage. Take care of any problems away.
- Cleaning: Remember to clean the inverter and the area, around it to prevent any buildup of dirt or debris using cleaning products and techniques to ensure the inverter stays in good condition.
- Temperature Control: Make sure the inverter is running at the temperature range its designed for and consider adding cooling options, like fans or ventilation if needed.
- Software Updates: Make sure to look for and install any software updates that’re available to ensure that the inverter runs smoothly with the up, to date features and enhancements.
- Professional Maintenance: Make sure to arrange maintenance appointments, with a technician to keep the inverter in top notch shape.
Return on Investment of Solar Inverters
Maximizing ROI with an Efficient Inverter
To maximize the efficiency of your panel system and increase your return, on investment (ROI), it is very important to have an inverter. Here’s the reason why it is important;
- Increased Energy Harvest: A designed inverter maximizes the transformation of panel generated DC power into AC power for household and commercial use efficiently. Better efficiency results in capturing and utilizing energy effectively resulting in savings and revenue generated from selling electricity.
- Longer Lifespan and Reliability: Good inverters are built to last long. Be dependable to minimize the chances of disruptions and upkeep expenses decreasing in the term which helps in saving money over time.
- Advanced Features and Functionality: In this day and age, inverters are equipped with capabilities like monitoring and diagnostics that aid in the upkeep of the solar system. This functionality can result in enhanced system efficiency and decreased operational expenses.
Government Incentives and Rebates for Solar Inverters
Countries worldwide, like China provide incentives and discounts to promote the use of power systems; this also helps boost the demand for solar inverters as a crucial element in the process.
- Subsidies and Tax Credits: Governments, at both local levels offer support like subsidies and tax benefits to encourage the adoption of solar power systems by reducing costs involved in setting them Up such as purchasing inverters.
- Rebate Programs: Certain authorities provide discounts, for parts of energy systems such as inverters which can help lower the overall cost, for both individuals and companies alike.
- Financing Options: Governments and financial institutions often provide low-interest loans or other financing options to make solar installations more affordable. These financing options can indirectly lower the cost of the inverter by spreading out the payments over time.
Conclusion
Selecting the inverter for your panels is a crucial choice that can influence the effectiveness and return, on investment of your entire solar power setup. By taking into account aspects like efficiency levels, compatibility, with components, warranty coverage and monitoring features while collaborating with an expert to accurately size and set up your inverter you can guarantee that your system runs smoothly and effectively over the long term.
FAQ
What is a solar power inverter?
A solar power inverter changes direct current (DC) from solar panels into alternating current (AC). Most homes and businesses use AC electricity; this makes the solar electricity usable for appliances and systems.
How does a solar inverter work?
A solar inverter takes DC electricity from solar panels and changes it to AC. This AC electricity powers home appliances or goes back into the grid. It also has a monitoring interface for performance and status.
What is the difference between a string inverter and a micro inverter for solar panels?
String inverters connect many solar panels together, making them cost-effective for big installations. Microinverters are on each panel, improving performance by working independently; they’re great for areas with changing shade.
What is a hybrid inverter for solar panels?
A hybrid inverter combines string and microinverters with battery storage; it lets you use stored energy during power outages or low solar production. This makes energy use more flexible.
What are power optimizers and how do they differ from inverters?
Power optimizers work with string inverters to boost each solar panel’s efficiency; they don’t convert DC to AC like inverters do. Instead, they maximize panel output before sending it to the inverter. This improves performance in different conditions.